Even so, Internet Explorer 11 is still installed as the default web browser with every version of Windows and Windows Server. To make matters worse, Windows 10 also shipped with non-Chromium Edge (now called Legacy Edge). You'll need to download and install a "modern" web browser, such as Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, FireFox, etc. Keep in mind that you can reload Internet Explorer sites with IE mode in Microsoft Edge.
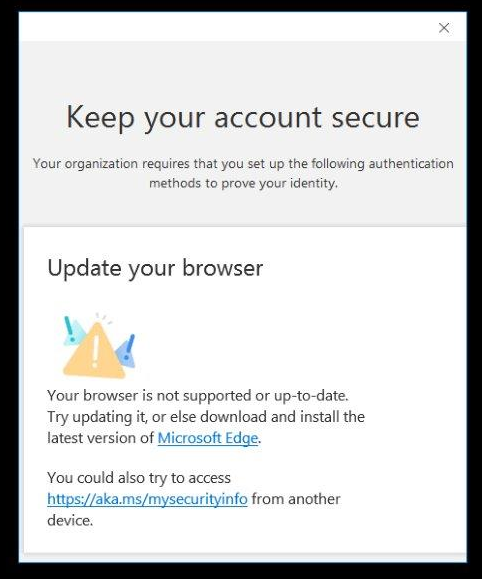
Even with ChrEdge (my name for Chromium Edge) installed as the default web browser, I've heard from a few customers that IE is still being used for some web work flows. For example, a customer recently showed me this MFA security confirmation prompt that is opening in IE for some reason.
All this leads me to the task at hand. How do you uninstall Internet Explorer 11 from Windows?
Run the following command from an elevated CMD or PowerShell prompt:
C:\Windows\System32\dism.exe /online /Disable-Feature /FeatureName:Internet-Explorer-Optional-amd64
Removal only takes a few seconds and the output looks like this:
DISM will prompt you to restart the computer to complete the operation. Until you do, Internet Explorer will still show as an available web browser. Optionally, you can add the /Quiet switch which will not show DISM uninstall progress and will automatically restart the computer when it's done.